Cummins diesel generator oil supply failure maintenance explanation
Troubleshooting and technical maintenance
Cummins diesel generator oil supply failure maintenance explanation
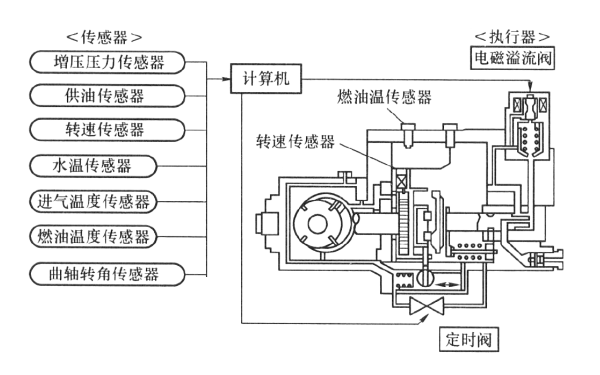
Fuel pump electronically controlled fuel supply system composition
1. Abnormal noise of diesel engine
If a certain part of the diesel engine fails, such as loose parts, imbalanced fitting clearance, abnormal combustion, etc., its initial manifestation during operation will be abnormal noise. Diesel engine noise generally comes from three aspects: combustion noise, fuel supply system noise and engine mechanical noise. Since abnormal noise is often difficult to accurately describe using language, words and tones, various abnormal noises can only be judged based on familiarity with the sound of normal operation.
(1) Burning roughly
The fuel quality is poor and the cetane number is too low; the fuel injection atomization condition worsens, and more fuel is put into combustion at the moment when it starts to ignite, causing the pressure in the cylinder to rise too quickly: the injection valve needle is stuck in the normally open position, The fuel injection is too early and the atomization is too poor, which can easily cause strong combustion noise.
(2) Fire knocking sound
Most of the problems are caused by incorrect injection advance angle, failure of the advance device, and excessive fuel supply, which causes the engine to produce knocking noises along with a large amount of smoke from the exhaust pipe during operation. The harder you press the accelerator, the louder the noise becomes. After the speed increases, the noise weakens, and the accelerator is quickly withdrawn to cause the engine to coast for a short period of time and the abnormal noise disappears, but the abnormal noise returns when it drops to idle speed.
(3) Abnormal noise caused by failure of the oil supply system
The injection advance angle is too small, the oil delivery valve spring is broken, the injector needle valve is not sealed, etc., which will cause the exhaust pipe to "shoot out". Lack of cylinders, water or air in the diesel fuel will cause the engine's operating sound to be discontinuous. When the fuel injector needle valve is stuck in the closed position, it will cause abnormal noise at the top of the fuel injection pump. When the plunger is stuck in the upper end position, it causes rack bite noise. When speeding, the fuel injection pump speed control lever was out of adjustment, causing the diesel engine to lose control and roar.
(4) Abnormal noise from the machine parts
While the engine is running, the noise gradually becomes louder and louder, or an abnormal noise suddenly occurs while the engine is running. This kind of noise generally increases as the speed increases. Even if the accelerator is sharply closed after acceleration, the noise still exists.
The reasons are:
① Cylinder knocking caused by excessive clearance between the piston and the cylinder;
② Impact sound caused by excessive wear of the timing gear;
③ Bearing ablation, journal wear, and bearing noise after loosening;
④ There are also transmission gear noises after the oil pump gears are worn, and the piston pins are loose and abnormal, etc.
(5) Diesel engine vibration and noise
Mainly due to its own weak support. Abnormal noise occurs once every working cycle of the engine, most of which are related to parts related to the camshaft (such as valves, timing gears, etc.). Abnormal noise occurs once every revolution of the engine, which is related to the parts of the crankshaft connecting rod mechanism. If abnormal noise occurs regularly and continuously, it usually occurs on rotating parts (such as flywheels, timing gears, etc.). Intermittent and irregular abnormal noises mostly come from engine accessory failures.
2. Diesel engine oil and gas leakage
1. Diesel engine oil leakage
The low-pressure oil circuit of the diesel generator fuel system consists of a fuel tank, a fuel transfer pump, a diesel filter, a fuel injection pump and its connecting pipelines. The pressure in the oil circuit from the fuel tank to the oil transfer pump is lower than atmospheric pressure, which is also called a negative pressure oil circuit. The oil circuit contains many parts and pipe joints, and leakage and seepage are easily caused during use. In addition, diesel oil leaks into the oil pan, which not only wastes fuel, but also affects the normal operation of the engine, so it must be repaired in time.
(1) Diesel leaks into the oil pan.
During use, it is often found that diesel oil is mixed into the oil pan, causing an increase in engine oil. This kind of internal leakage is a common failure phenomenon of diesel engines.
Diesel as a power source cannot be fully burned in the combustion chamber to perform work, but flows into the oil pan through various channels such as the cylinder wall. Obviously, internal leakage of diesel oil not only weakens the engine's power performance, but also seriously affects and destroys the oil drilling and pressure, and aggravates the wear of various engine components.
The main reason for the internal leakage of the diesel engine is that the diesel fuel burns poorly during its operation and flows into the oil pan through the gap between the piston and the cylinder wall. The reasons for poor diesel combustion are: first, insufficient diesel injection pressure and poor spray conditions; second, poor cylinder sealing, and the gas pressure in the compression stroke is too low to allow the mixture of diesel and air to reach the level of compression ignition.
(2) Oil leakage from low-pressure oil line.
In the low-pressure oil circuit, only the section from the fuel pump to the fuel injection pump may leak oil, while the pressure in the section from the fuel tank to the fuel pump is lower than atmospheric pressure, so there may be air leakage, but there will be no oil leakage.
The main causes of low-pressure oil circuit leakage are:
① The oil pump ejector is severely worn;
② The oil pipe is damaged;
③ The joints are not fastened properly;
④ The positioning screw of the fuel injection pump plunger sleeve is poorly sealed;
⑤ The low-pressure oil-blocking rubber ring on the tight seat of the oil outlet valve is aging;
⑥ The interface between the plunger and the pump body is uneven, etc.
Oil leakage mostly leaks out from the inside of the oil pipes or parts of the low-pressure oil circuit. The leakage location can be determined by observing the oil traces.
(3) Inspection of diesel engine diesel leakage
① Check whether the rubber ring installed on the fuel injector is sealed;
② Replace the cylinder gasket;
③ Check and adjust the oil supply timing;
④ Check the sealing condition of valve and valve seat;
⑤ Adjust the valve clearance;
⑥ Check the spray condition of the fuel injector, and adjust the high-pressure oil pump and fuel injector if necessary;
⑦ Check the piston and cylinder clearance, and replace the piston, piston ring or cylinder liner if necessary;
⑧ Check the components or oil pipes of the low-pressure oil circuit, if any leakage is found, find out the cause and repair it.
2. Diesel engine air leakage
Determination of the phenomenon of air entering the low-pressure oil line: The fuel of the diesel engine is sucked out from the fuel tank by the oil transfer pump and transported to the fuel injection pump. If the oil line leaks air, the oil transfer pump will not be able to transfer fuel. Air is elastic and compressible. When air exists in the oil circuit of the diesel engine fuel supply system, the bubbles will change in volume as the fuel injection pump plunger reciprocates. When the plunger is in the compression stroke, the bubbles are compressed, preventing the oil pressure from rising to the specified injection pressure. When the plunger is in the oil suction stroke, the bubbles expand and return to their original volume, so that no suction can be generated in the oil circuit. Therefore, the presence of air will cause insufficient or even interruption of oil supply.
The engine gradually stalls during operation and fails to ignite when restarted after stalling. Open the bleed screw of the high-pressure oil pump, pump the oil with a hand oil pump, remove the air in the oil line, and then start the engine and it will catch fire. However, if it stalls again after a while, it can be determined that air has entered the oil line.
In addition to the fact that the oil level in the tank is so low that it is close to the oil suction port, causing air to enter the oil pipe, the air leakage points in this section of the oil line are mostly at the oil pipe joints of the oil transfer pump. Generally, the copper gasket is damaged or improperly installed.
When the diesel engine is working, the pressure in the oil line from the fuel delivery pump to the fuel injection pump is higher than the atmospheric pressure. Even if there is a leakage point in the oil line, it will only leak oil but not air, so it will not affect the normal operation of the engine. However, when the engine stalls, oil seeps out from the leakage point, causing the oil pressure higher than atmospheric pressure to be maintained, and even causing air backflow, making it difficult to start again. In order to confirm whether there is air leakage in this section, you can use an oil pipe from the fuel pump to skip the diesel filter and connect it directly to the fuel injection pump. Then start the engine after exhaust and observe. If the fault disappears, you can determine that there is a leakage point in this section of the oil line. . If the fault still exists, it may be caused by oil leakage from the simple positioning screw, bleed screw, etc. of the fuel injection pump plunger sleeve. Troubleshooting of air leakage in low-pressure oil lines: When encountering air leakage in low-pressure oil lines, first check whether the bleed screws on the diesel filter, fuel injection pump, etc. are tightened, and then check each pipe joint in the oil line, especially the hose part. Open the air bleed screw, use a hand oil pump to remove the air from the oil circuit, tighten each pipe joint, and remove any loose seals. When replacing the filter element or cleaning the oil-water separator, a large amount of air will also enter the low-pressure oil line, so air mixing must be performed. When the fuel transfer pump pumps out all diesel without bubbles, you can tighten the bleed bolt. Then start the engine, check all parts for air leaks, and repair them if necessary until there are no leaks.
3. Abnormal smoke exhaust from diesel engine
When the diesel generator is under load, it runs unevenly and black smoke or white smoke is emitted from the exhaust pipe.
(1) Exhaust black smoke
Black smoke is generally caused by: excessive fuel supply from the fuel injection pump or uneven fuel supply to each cylinder: premature fuel injection: clogged air filter, resulting in insufficient air intake; poor spray quality of the fuel injector or fuel injection Oil dripping from the piston ring; excessive wear of the piston rings or corresponding gaps between the rings: abnormality of the speed regulator: improper adjustment of the maximum oil quantity limit screw, etc.
First remove the air filter and observe the exhaust smoke color. If the smoke exhaust condition improves, the fault is caused by serious dirt on the air filter. Then check whether the oil supply time is too early. When the engine is running, you can perform a cylinder-by-cylinder oil cutoff test. When a cylinder cuts off oil, first remove the air filter and observe the exhaust smoke color. If the smoke exhaust condition improves, the fault is caused by a dirty air filter. Then check whether the oil supply time is too early, and perform a cylinder-by-cylinder oil cutoff test while the engine is running. When a cylinder cuts off oil, the engine speed decreases, the black smoke decreases significantly, and the knocking sound weakens or disappears, indicating that the cylinder has too much oil supply plate. If the engine speed changes little and the black smoke disappears, it indicates that the spray quality of the injector in this cylinder is poor. After finding the faulty cylinder, disassemble and inspect the injector. If necessary, a new injector can be installed for comparison. If the fault cannot be eliminated by using the above method, if the fuel injection pump plunger tappet has an adjustment screw, check whether the fuel injection in each cylinder is consistent and make adjustments if necessary. When checking whether the fuel supply amount of the fuel injection pump is excessive and the unevenness of the fuel supply meets the standards, it should be carried out on the test bench.
(2) Exhaust white smoke
White smoke is mostly caused by poor spraying, which prevents the fuel from being burned and is discharged as white smoke.
The main reasons causing diesel engines to emit white smoke are: failure of the starting preheating device and too low engine temperature; inaccurate fuel injection timing; blocked air intake passages and insufficient air supply; too much or too little fuel supply from the fuel injection pump; fuel injection The fuel injection atomization of the fuel injection pump is poor, and the mixture formation quality is poor; the cylinder pressure is too low, and the conditions for diesel self-ignition are poor; the fuel injection of each branch of the fuel injection pump is inconsistent; the spray is poor, the fuel injector is dripping; there is water or air in the fuel system, etc.
White smoke can be checked by cylinder-by-cylinder oil cut-off method to find the faulty injector and adjust its injection pressure. If the exhaust emits white smoke and the engine is weak and prone to overheating, it means that the fuel injection is too late and the fuel injection timing should be adjusted. Check whether the low-temperature starting preheating device is intact. If it still cannot start, check and adjust the injection timing and fuel supply amount. Then check the atomization of the fuel injection, whether the injector needle valve is stuck, and whether the cylinder pressure is too low.
4. Diesel engine stalls on its own
(1) Diagnosis of diesel engine self-shutdown fault
The characteristics of the diesel generator's self-extinguishing fault are: it gradually becomes weak during operation, and finally slowly self-extinguishing. The main reason is that the fuel supply is interrupted and the fuel supply is not available. The reasons are mostly: there is no oil in the fuel tank; the vent hole of the fuel tank is blocked; the oil transfer pump does not work; there is air in the oil line; the overflow valve is damaged, etc. In this case, first check whether there is oil in the fuel tank and whether the vent hole of the fuel tank is unobstructed. Then loosen the bleed screw of the fuel injection pump and pump the oil with a hand oil pump. Check whether air has entered the oil line and whether the oil line is unobstructed. If necessary, find the leakage. Gas or blockage area. Finally, check whether the oil transfer pump and relief valve are functioning normally, and replace the assembly if necessary.
If the diesel engine suddenly stalls during operation and cannot be started again, this is mostly due to damage to the relevant mechanical parts. The semicircular key of the fuel injection pump drive shaft is cut off, or the bakelite transmission part of the coupling is damaged, causing the fuel injector to not work; the fuel injection pump operating tie rod The connecting pins are loose, the fixing bolts between the fuel injection pump drive shaft and the drive plate are loose, and the fuel injection pump cannot be driven; the diesel engine holds the cylinder or burns the shaft, and the fuel injection pump drive strip is broken. When encountering this phenomenon, first start the engine and check whether the coupling part is intact, then check whether the semicircular key of the fuel injection pump drive shaft is damaged, and repair it if necessary. If the crankshaft does not rotate, it may be that the piston is holding the cylinder, the tile is burning, the shaft is holding, or the drive chain is broken, etc. Find the cause and fix it.
(2) Measures to prevent diesel engine self-extinguishing failure
During use, add high-quality fuel as much as possible, check the oil line regularly, clear it with high-pressure air, and drain the air in the low-pressure oil line before starting. If the oil pipe is found to be ruptured, it should be repaired or replaced with new parts in time. During maintenance, clean the oil outlet valve, replace the broken oil outlet valve spring, check the oil pump spring, injector needle valve, speed regulating spring, etc. and repair any abnormalities found in time to eliminate the hidden danger of the diesel engine's self-shutdown failure and ensure safe operation.
5. Diesel engine periodic "travel train"
1. Failure phenomena and hazards
Diesel generator, "wandering" is also called "wheezing", which is a manifestation of unstable diesel engine speed.
(1) The phenomenon is: when the diesel engine is running at idle or medium speed, it shows periodic and regular changes of fast and slow, and the change is not timely when increasing or decreasing the throttle, and the engine is weak; at the same time, the engine makes a loud noise during operation. The rhythm is high and low, the speed fluctuates greatly, and the sound is clearly distinguishable.
(2) Periodic "wandering" occurs in the diesel engine. If it is not eliminated in time, it will become more and more serious. It will not only reduce the economic performance of the diesel engine, but also cause the diesel engine to work unstable, aggravate the wear and tear of the parts and rapid fatigue, thus affecting the performance of the diesel engine. The reliability of the diesel engine is very important. In severe cases, the diesel engine will not be able to work normally.
2. Cause of failure
Periodic wandering of the diesel engine is essentially the destruction of the normal speed regulating function of the diesel engine. It is usually caused by excessive movement resistance from the fuel injection pump to the moving parts in the governor, which reduces the sensitivity of the governor or causes gaps in the fit of its internal parts. If it is too large, the change in fuel supply will lag behind the change in speed. The reasons for the failure are: the lubricating oil is not clean or poorly lubricated; foreign matter enters the mating surface, causing the speed control rod to become stiff or the resistance increases; the internal parts or working surfaces of the speed regulator are severely worn, resulting in excessive resistance of the speed regulator. ; The speed regulator is improperly adjusted and the parts are too tight; the oil supply pull rod is not flexible; too much engine oil is added to the speed regulator, and the expansion and contraction of the centrifugal block is hindered due to the damping effect of the oil and the sensitivity of the speed regulator decreases; The wear of each connection point exceeds the limit, the fit is loose, and the gap increases; the injection timing is inaccurate, the atomization is poor, and the injection pressure of the nozzle is uneven, etc.
3. Fault diagnosis method
(1) The main fault diagnosis methods for periodic wandering of diesel engines are: If there is a slight "wandering" at idle speed, you can continue to use it. If it is serious, you should remove the upper cover of the speed regulator and observe the front and rear movement of the pump rod. quantity.
(2) Remove the side cover of the fuel injection pump, hold the pump rod with your fingers and move it back and forth to check its tightness. If the rod does not move, it should be repaired to make it move flexibly. If the pump rod can only move within a very small range, it is usually caused by the inflexible rotation of the plunger or the tightness of the connections between the pump rod and the pump rod, and should be repaired and eliminated. If the pump rod can move flexibly, use the other hand to hold the pull arm of the pump rod to keep it stationary, and hold the pump rod with one hand to move. If you feel a certain amount of looseness, it may be that the joints of the speed regulating mechanism are loose, and further inspection is required. eliminate.
(3) If the pump rod is tight during movement, the fault may be in the plunger. You can loosen the plunger limit screw. If the pump rod moves flexibly, it is because the screw head is pressing against the plunger jacket. You can remove the screw. Next, add a gasket of a certain thickness, and then tighten it firmly. If there is still no improvement after loosening the limit screw of the plunger jacket, loosen the tight seat of the oil delivery valve. If there is improvement, it is because the torque of the tight seat of the oil delivery valve is too large. If there is still no improvement, the plunger jacket should be removed. Check whether there is any dirt on the fitting part, clean it if necessary and then reinstall it. Check whether there is too much oil in the governor; check whether there is fuel leakage; whether there is air in the oil circuit; adjust the flyweight stroke of the governor and the pretension of the speed regulating spring, and adjust the injection timing and injection pressure if necessary , to meet the requirements of the specification.





